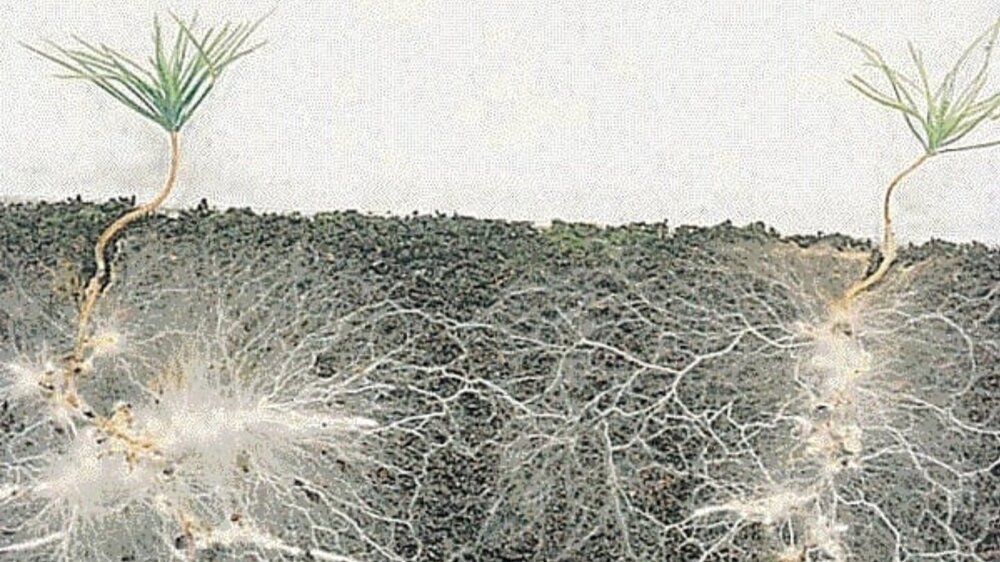
A Mycorrhizal network (also known as a common mycorrhizal network or CMN) is an underground network found in forests and other plant communities, created by the hyphae of mycorrhizal fungi joining with plant roots. This network connects individual plants together and transfers water, carbon, nitrogen, and other nutrients and minerals between participants. Several studies have demonstrated that mycorrhizal networks can transport carbon, phosphorus, nitrogen, water, defense compounds, and allelochemicals from plant to plant. The flux of nutrients and water through hyphal networks has been proposed to be driven by a source–sink model, where plants growing under conditions of relatively high resource availability (e.g., high-light or high-nitrogen environments) transfer carbon or nutrients to plants located in less favorable conditions. A common example is the transfer of carbon from plants with leaves located in high-light conditions in the forest canopy, to plants located in the shaded understory where light availability limits photosynthesis. In natural ecosystems, plants may be dependent on fungal symbionts for 90% of their phosphorus requirements and 80% of their nitrogen requirements. Mycorrhizal relationships are most commonly mutualistic, with both partners benefiting, but can be commensal or parasitic, and a single partnership may change between any of the three types of symbiosis at different times.
The formation and nature of these networks, is context-dependent, and can be influenced by factors such as soil fertility, resource availability, host or myco-symbiont genotype, disturbance and seasonal variation. Some plant species, such as buckhorn plantain, a common lawn and agricultural weed, benefit from mycorrhizal relationships in conditions of low soil fertility, but are harmed in higher soil fertility. Both plants and fungi associate with multiple symbiotic partners at once, and both plants and fungi are capable of preferentially allocating resources to one partner over another.
Referencing an analogous function served by the World Wide Web in human communities, the many roles that mycorrhizal networks appear to play in woodland have earned them a colloquial nickname: the Wood Wide Web.
Types
There are two main types of mycorrhizal networks: arbuscular mycorrhizal networks and ectomycorrhizal networks.
- Arbuscular mycorrhizal networks are formed between plants that associate with glomeromycetes. Arbuscular mycorrhizal associations (also called endomycorrhizas) predominate among land plants, and are formed with 150–200 known fungal species, although true fungal diversity may be much higher.[16] It has generally been assumed that this association has low host specificity. However, recent studies have demonstrated preferences of some host plants for some glomeromycete species
- Ectomycorrhizal networks are formed between plants that associate with ectomycorrhizal fungi and proliferate by way of ectomycorrhizal extramatrical mycelium. In contrast to glomeromycetes, ectomycorrhizal fungal are a highly diverse and polyphyletic group consisting of 10,000 fungal species. These associations tend to be more specific, and predominate in temperate and boreal forests.
Mycoheterotrophic and mixotrophic plants
Monotropastrum humile—an example of a myco-heterotrophic plant that gains all of its energy through mycorrhizal networks
Myco-heterotrophic plants are plants that are unable to photosynthesize and instead rely on carbon transfer from mycorrhizal networks as their main source of energy.[20] This group of plants includes about 400 species. Some families that include mycotrophic species are: Ericaceae, Orchidaceae and Gentianaceae. In addition, mixotrophic plants also benefit from energy transfer via hyphal networks. These plants have fully developed leaves but usually live in very nutrient and light limited environments that restrict their ability to photosynthesize.
Plants and fungi communicate via mycorrhizal networks with other plants or fungi of the same or different species. Mycorrhizal networks allow for the transfers of signals and cues between plants which influence the behavior of the connected plants by inducing morphological or physiological changes. The chemical substances which act as these signals and cues are referred to as infochemicals. These can be allelochemicals, defensive chemicals or nutrients. Allelochemicals are used by plants to interfere with the growth or development of other plants or organisms, defensive chemicals can help plants in mycorrhizal networks defend themselves against attack by pathogens or herbivores, and transferred nutrients can affect growth and nutrition. Results of studies which demonstrate these modes of communication have led the authors to hypothesize mechanisms by which the transfer of these nutrients can affect the fitness of the connected plants.
Communication
Reports discuss the ongoing debate within the scientific community regarding what constitutes communication, but the extent of communication influences how a biologist perceives behaviors. Communication is commonly defined as imparting or exchanging information. Biological communication, however, is often defined by how fitness in an organism is affected by the transfer of information in both the sender and the receiver. Signals are the result of evolved behavior in the sender and effect a change in the receiver by imparting information about the sender’s environment. Cues are similar in origin but only effect the fitness of the receiver. Both signals and cues are important elements of communication, but workers maintain caution as to when it can be determined that transfer of information benefits both senders and receivers. Thus, the extent of biological communication can be in question without rigorous experimentation.[23] It has, therefore, been suggested that the term infochemical be used for chemical substances which can travel from one organism to another and elicit changes. This is important to understanding biological communication where it is not clearly delineated that communication involves a signal that can be adaptive to both sender and receiver.
Behavior and information transfer
A morphological or physiological change in a plant due to a signal or cue from its environment constitutes behavior in plants, and plants connected by a mycorrhizal network have the ability to alter their behavior based on the signals or cues they receive from other plants. These signals or cues can be biochemical, electrical, or can involve nutrient transfer. Plants release chemicals both above- and below-ground to communicate with their neighbors to reduce damage from their environment. Changes in plant behavior invoked by the transfer of infochemicals vary depending on environmental factors, the types of plants involved and the type of mycorrhizal network. In a study of orange seedlings, mycorrhizal networks acted to transfer infochemicals, and the presence of a mycorrhizal network affected the growth of plants and enhanced production of signaling molecules. One argument in support of the claim mycorrhizal can transfer various infochemicals is that they have been shown to transfer molecules such as lipids, carbohydrates and amino acids. Thus, transfer of infochemicals via mycorrhizal networks can act to influence plant behavior.
There are three main types of infochemicals shown to act as response inducing signals or cues by plants in mycorrhizal networks, as evidenced by increased effects on plant behavior: allelochemicals, defensive chemicals and nutrients.
Allelopathic communication
Allelopathy is the process by which plants produce secondary metabolites known as allelochemicals, which can interfere with the development of other plants or organisms. Allelochemicals can affect nutrient uptake, photosynthesis and growth; furthermore, they can down regulate defense genes, affect mitochondrial function, and disrupt membrane permeability leading to issues with respiration.
Plants produce many types of allelochemicals, such as thiopenes and juglone, which can be volatilized or exuded by the roots into the rhizosphere. Plants release allelochemicals due to biotic and abiotic stresses in their environment and often release them in conjunction with defensive compounds. In order for allelochemicals to have a detrimental effect on a target plant, they must exist in high enough concentrations to be toxic, but, much like animal pheromones, allelochemicals are released in very small amounts and rely on the reaction of the target plant to amplify their effects. Due to their lower concentrations and the ease in which they are degraded in the environment, the toxicity of allelochemicals is limited by soil moisture, soil structure, and organic matter types and microbes present in soils. The effectiveness of allelopathic interactions has been called into question in native habitats due to the effects of them passing through soils, but studies have shown that mycorrhizal networks make their transfer more efficient. These infochemicals are hypothesized to be able to travel faster via mycorrhizal networks, because the networks protect them from some hazards of being transmitted through the soil, such as leaching and degradation. This increased transfer speed is hypothesized to occur if the allelochemicals move via water on hyphal surfaces or by cytoplasmic streaming. Studies have reported concentrations of allelochemicals two to four times higher in plants connected by mycorrhizal networks. Thus, mycorrhizal networks can facilitate the transfer of these infochemicals.
Studies have demonstrated correlations between increased levels of allelochemicals in target plants and the presence of mycorrhizal networks. These studies strongly suggest that mycorrhizal networks increase the transfer of allelopathic chemicals and expand the range, called the bio-active zone, in which they can disperse and maintain their function.[24] Furthermore, studies indicate increased bio-active zones aid in the effectiveness of the allelochemicals because these infochemicals cannot travel very far without a mycorrhizal network. There was greater accumulation of allelochemicals, such as thiopenes and the herbicide imazamox, in target plants connected to a supplier plant via a mycorrhizal network than without that connection, supporting the conclusion that the mycorrhizal network increased the bio-active zone of the allelochemical. Allelopathic chemicals have also been demonstrated to inhibit target plant growth when target and supplier are connected via AM networks. The black walnut is one of the earliest studied examples of allelopathy and produces juglone, which inhibits growth and water uptake in neighboring plants. In studies of juglone in black walnuts and their target species, the presence of mycorrhizal networks caused target plants to exhibit reduced growth by increasing the transfer of the infochemical. Spotted knapweed, an allelopathic invasive species, provides further evidence of the ability of mycorrhizal networks to contribute to the transfer of allelochemicals. Spotted knapweed can alter which plant species a certain AM fungus prefers to connect to, changing the structure of the network so that the invasive plant shares a network with its target. These and other studies provide evidence that mycorrhizal networks can facilitate the effects on plant behavior caused by allelochemicals.
Defensive communication
Mycorrhizal networks can connect many different plants and provide shared pathways by which plants can transfer infochemicals related to attacks by pathogens or herbivores, allowing receiving plants to react in the same way as the infected or infested plants. A variety of plant derived substances act as these infochemicals.
When plants are attacked they can manifest physical changes, such as strengthening their cell walls, depositing callose, or forming cork. They can also manifest biochemical changes, including the production of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or the up-regulation of genes producing other defensive enzymes, many of which are toxic to pathogens or herbivores. Salicylic acid (SA) and its derivatives, like methyl salicylate, are VOCs which help plants to recognize infection or attack and to organize other plant defenses, and exposure to them in animals can cause pathological processes. Terpenoids are produced constituently in many plants or are produced as a response to stress and act much like methyl salicylate. Jasmonates are a class of VOCs produced by the jasmonic acid (JA) pathway. Jasmonates are used in plant defense against insects and pathogens and can cause the expression of proteases, which defend against insect attack. Plants have many ways to react to attack, including the production of VOCs, which studies report can coordinate defenses among plants connected by mycorrhizal networks.
Many studies report that mycorrhizal networks facilitate the coordination of defenses between connected plants using volatile organic compounds and other plant defensive enzymes acting as infochemicals.
Priming occurs when a plant’s defenses are activated before an attack. Studies have shown that priming of plant defenses among plants in mycorrhizal networks may be activated by the networks, as they make it easier for these infochemicals to propagate among the connected plants. The defenses of uninfected plants are primed by their response via the network to the terpenoids produced by the infected plants. AM networks can prime plant defensive reactions by causing them to increase the production of terpinoids.
In a study of tomato plants connected via an AM mycorrhizal network, a plant not infected by a fungal pathogen showed evidence of defensive priming when another plant in the network was infected, causing the uninfected plant to up-regulate genes for the SA and JA pathways. Similarly, aphid-free plants were shown to only be able to express the SA pathways when a mycorrhizal network connected them to infested plants. Furthermore, only then did they display resistance to the herbivore, showing that the plants were able to transfer defensive infochemicals via the mycorrhizal network.
Many insect herbivores are drawn to their food by VOCs. When the plant is consumed, however, the composition of the VOCs change, which can then cause them to repel the herbivores and attract insect predators, such as parasitoid wasps. Methyl salicylate was shown to be the primary VOC produced by beans in a study which demonstrated this effect. It was found to be in high concentrations in infested and uninfested plants, which were only connected via a mycorrhizal network. A plant sharing a mycorrhizal network with another that is attacked will display similar defensive strategies, and its defenses will be primed to increase the production of toxins or chemicals which repel attackers or attract defensive species.
In another study, introduction of budworm to Douglas fir trees led to increased production of defensive enzymes in uninfested ponderosa pines connected to the damaged tree by an ECM network. This effect demonstrates that defensive infochemicals transferred through such a network can cause rapid increases in resistance and defense in uninfested plants of a different species.
The results of these studies support the conclusion that both ECM and AM networks provide pathways for defensive infochemicals from infected or infested hosts to induce defensive changes in uninfected or uninfested conspecific and heterospecific plants, and that some recipient species generally receive less damage from infestation or infection.
Decoding
A study decoded electrical communication between fungi into word-like components via spiking characteristics.
The spiking characteristics were specific to the fungi species and were often clustered into sentence-like series. The study found that size of fungal lexicon can be up to 50 words in the four investigated species while the most frequently used ones do not exceed 15–20 words. However, the meaning or informational content, if there is any, remains unknown.
Nutrient transfer
Numerous studies have reported that carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus are transferred between conspecific and heterospecific plants via AM and ECM networks. Other nutrients may also be transferred, as strontium and rubidium, which are calcium and potassium analogs respectively, have also been reported to move via an AM network between conspecific plants. Scientists believe that transfer of nutrients by way of mycorrhizal networks could act to alter the behavior of receiving plants by inducing physiological or biochemical changes, and there is evidence that these changes have improved nutrition, growth and survival of receiving plants.
Mechanisms
Several mechanisms have been observed and proposed by which nutrients can move between plants connected by a mycorrhizal network, including source-sink relationships, preferential transfer and kin related mechanisms.
Transfer of nutrients can follow a source-sink relationship where nutrients move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. An experiment with grasses and forbs from a California oak woodland showed that nutrients were transferred between plant species via an AM mycorrhizal network, with different species acting as sources and sinks for different elements.Nitrogen has also been shown to flow from nitrogen-fixing plants to non-nitrogen fixing plants through a mycorrhizal network following a source-sink relationship.
It has been demonstrated that mechanisms exist by which mycorrhizal fungi can preferentially allocate nutrients to certain plants without a source-sink relationship. Studies have also detailed bi-directional transfer of nutrients between plants connected by a network, and evidence indicates that carbon can be shared between plants unequally, sometimes to the benefit of one species over another.
Kinship can act as another transfer mechanism. More carbon has been found to be exchanged between the roots of more closely related Douglas firs sharing a network than more distantly related roots. Evidence is also mounting that micronutrients transferred via mycorrhizal networks can communicate relatedness between plants. Carbon transfer between Douglas fir seedlings led workers to hypothesize that micronutrient transfer via the network may have increased carbon transfer between related plants.
These transfer mechanisms can facilitate movement of nutrients via mycorrhizal networks and result in behavioral modifications in connected plants, as indicated by morphological or physiological changes, due to the infochemicals being transmitted. One study reported a three-fold increase in photosynthesis in a paper birch transferring carbon to a Douglas fir, indicating a physiological change in the tree which produced the signal. Photosynthesis was also shown to be increased in Douglas fir seedlings by the transport of carbon, nitrogen and water from an older tree connected by a mycorrhizal network. Furthermore, nutrient transfer from older to younger trees on a network can dramatically increase growth rates of the younger receivers. Physiological changes due to environmental stress have also initiated nutrient transfer by causing the movement of carbon from the roots of the stressed plant to the roots of a conspecific plant over a mycorrhizal network.Thus, nutrients transferred through mychorrhizal networks act as signals and cues to change the behavior of the connected plants.
Evolutionary and adaptational perspectives
It is hypothesized that fitness is improved by the transfer of infochemicals through common mycorrhizal networks, as these signals and cues can induce responses which can help the receiver survive in its environment. Plants and fungus have evolved heritable genetic traits which influence their interactions with each other, and experiments, such as one which revealed the heritability of mycorrhizal colonization in cowpeas, provide evidence. Furthermore, changes in behavior of one partner in a mycorrhizal network can affect others in the network; thus, the mycorrhizal network can provide selective pressure to increase the fitness of its members.
Adaptive mechanisms
Although they remain to be vigorously demonstrated, workers have suggested mechanisms which might explain how transfer of infochemicals via mycorrhizal networks may influence the fitness of the connected plants and fungi.
A fungus may preferentially allocate carbon and defensive infochemicals to plants that supply it more carbon, as this would help to maximize its carbon uptake. This may happen in ecosystems where environmental stresses, such as climate change, cause fluctuations in the types of plants in the mycorrhizal network. A fungus might also benefit its own survival by taking carbon from one host with a surplus and giving it to another in need, thus it would insure the survival of more potential hosts and leave itself with more carbon sources should a particular host species suffer. Thus, preferential transfer could improve fungal fitness.
Plant fitness may also be increased in several ways. Relatedness may be a factor, as plants in a network are more likely to be related; therefore, kin selection might improve inclusive fitness and explain why a plant might support a fungus that helps other plants to acquire nutrients. Receipt of defensive signals or cues from an infested plant would be adaptive, as the receiving plant would be able to prime its own defenses in advance of an attack by herbivores. Allelopathic chemicals transferred via CMNs could also affect which plants are selected for survival by limiting the growth of competitors through a reduction of their access to nutrients and light. Therefore, transfer of the different classes of infochemicals might prove adaptive for plants.
Seedling establishment
Mature Douglas fir
Seedling establishment research often is focused on forest level communities with similar fungal species. However mycorrhizal networks may shift intra- and interspecific interactions that may alter pre-established plants physiology. Shifting competition can alter the evenness and dominance of the plant community. Discovery of seedling establishment showed seedling preference is near existing plants of con-or heterospecific species and seedling amount is abundant. Many believe the process of new seedlings becoming infected with existing mycorrhizae expedite their establishment within the community. The seedling inherit tremendous benefits from their new formed symbiotic relation with the fungi. The new influx of nutrients and water availability, help the seedling with growth but more importantly help ensure survival when in a stressed state. Mycorrhizal networks aid in regeneration of seedlings when secondary succession occurs, seen in temperate and boreal forests.
| Increased infectivity range of diverse mycorrhizal fungi |
|---|
| Increased carbon inputs from mycorrhizal networks with other plants |
| Increased area means greater access to nutrients and water |
| Increased exchange rates of nutrients and water from other plants. |
Several studies have focused on relationships between mycorrhizal networks and plants, specifically their performance and establishment rate. Douglas fir seedlings’ growth expanded when planted with hardwood trees compared to unamended soils in the Oregon Mountains. Douglas firs had higher rates of ectomycorrhizal fungal diversity, richness, and photosynthetic rates when planted alongside root systems of mature Douglas firs and Betula papyrifera than compared to those seedlings who exhibited no or little growth when isolated from mature trees. The Douglas fir was the focus of another study to understand its preference for establishing in an ecosystem. Two shrub species, Arctostaphylos and Adenostoma both had the opportunity to colonize the seedlings with their ectomycorrhizae fungi. Arctostaphylos shrubs colonized Douglas fir seedlings who also had higher survival rates. The mycorrhizae joining the pair had greater net carbon transfer toward the seedling. The researchers were able to minimize environmental factors they encountered in order to avoid swaying readers in opposite directions.
In burned and salvaged forest, Quercus rubrum L. establishment was facilitated when acorns were planted near Q. montana but did not grow when near arbuscular mycorrhizae Acer rubrum L. Seedlings deposited near Q. montana had a greater diversity of ectomycorrhizal fungi, and a more significant net transfer of nitrogen and phosphorus contents demonstrating ectomycorrhizal fungi formation with the seedling helped with their establishment. Results demonstrated with increasing density; mycorrhizal benefits decrease due to an abundance of resources that overwhelmed their system resulting in little growth as seen in Q. rubrum.
Mycorrhizae networks decline with increasing distance from parents, but rate of survival was unaffected. This indicated that seedling survival has a positive relation with decreasing competition as networks move out farther.
One study displayed the effects of ectomycorrhizal networks in plants who face primary succession. In his experiment, Nara transplanted Salix reinii seedlings inoculated with different ectomycorrhizal species. He found that mycorrhizal networks are the connection of ectomycorrhizal fungi colonization and plant establishment. Results showed increased biomass and survival of germinates near the inoculated seedlings compared to inoculated seedlings.
Studies have found that association with mature plant equates with higher survival of the plant and greater diversity and species richness of the mycorrhizal fungi.
Carbon transfer
Carbon transfer has been demonstrated by experiments using isotopic 14C and following the pathway from ectomycorrhizal conifer seedlings to another using mycorrhizal networks. The experiment showed a bidirectional movement of the 14C within ectomycorrhizae species. Further investigation of bidirectional movement and the net transfer was analyzed using pulse labeling technique with isotopes 13C and 14C in ectomycorrhizal species Douglas fir and Betula payrifera seedlings. Results displayed an overall net balance of carbon transfer between the two until the second year where the Douglas fir received carbon from B. payrifera. Detection of the isotopes was found in receiver plant shorts, expressing carbon transfer from fungus to plant tissues.
When ectomycorrhizal fungi receiver end of the plant has limited sunlight availability, there was an increase in carbon transfer, indicating a source-sink gradient of carbon among plants and shade surface area regulates carbon transfer.
Water transfer
In arid regions, many plant species have been shown to survive drought using mycorrhizal networks. Plant species have been found with ectomycorrhizae penetrating deep into bedrock, extracting water from the bedrock itself as the fungi decompose the stone. Isotopic tracers and fluorescent dyes have been used to establish the water transfer between conspecific or heterospecific plants. The hydraulic lift aids in water transfer from deep-rooted trees to seedlings, which means some participants in the mycorrhizal network could experience a detrimental effect.
Importance
Several positive effects of mycorrhizal networks on plants have been reported. These include increased establishment success, higher growth rate and survivorship of seedlings; improved inoculum availability for mycorrhizal infection; transfer of water, carbon, nitrogen and other limiting resources increasing the probability for colonization in less favorable conditions. In fact, a <1% increase in carbon has been shown to create up to 4x increase in new seedlings. These benefits have also been identified as the primary drivers of positive interactions and feedbacks between plants and mycorrhizal fungi that influence plant species abundance.
Connection to mycorrhizal networks creates positive feedbacks between adult trees and seedlings of the same species and can disproportionally increase the abundance of a single species, potentially resulting in monodominance. Monodominance occurs when a single tree species accounts for the majority of individuals in a forest stand. McGuire (2007), working with the monodominant tree Dicymbe corymbosa in Guyana demonstrated that seedlings with access to mycorrhizal networks had higher survival, number of leaves, and height than seedlings isolated from the ectomycorrhizal networks.
See also
- Entangled Life (book)
- Forest ecology
- Suzanne Simard
- Symbiosis
- Mutualism (biology)
- Plant communication
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycorrhizal_network
Underground Networking: The Amazing Connections Beneath Your Feet
Walking through the forest, it’s easiest to pay attention to what is happening at eye level and above. Birds, sunlight, wind, branches, there’s a lot to observe. Next time you’re exploring a forest, consider what lies below the soil, leaves, and moss that carpet the ground. Underneath the forest floor, intertwined with the roots of the trees, is a fascinating microscopic network of fungus.
Woodwide Web
When most of us think of fungus, we imagine mushrooms sprouting out of the ground. Those mushrooms are in fact the “fruit” of the fungus, while the majority of the fungal organism lives in the soil interwoven with tree roots as a vast network of mycelium. Mycelium are incredibly tiny “threads” of the greater fungal organism that wrap around or bore into tree roots. Taken together, myecelium composes what’s called a “mycorrhizal network,” which connects individual plants together to transfer water, nitrogen, carbon and other minerals. German forester Peter Wohlleben dubbed this network the “woodwide web,” as it is through the mycelium that trees “communicate.”
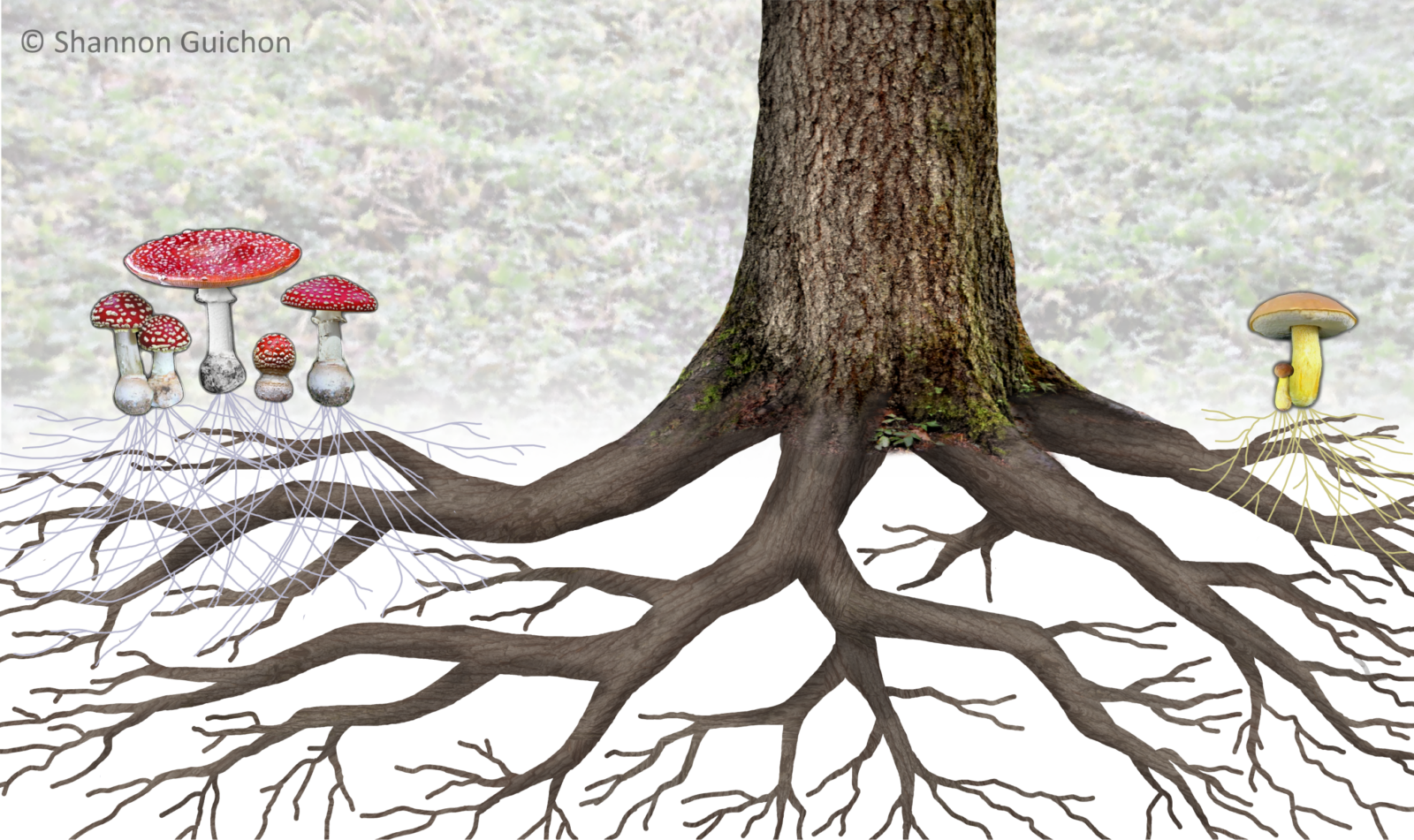

In healthy forests, each tree is connected to others via this network, enabling trees to share water and nutrients. For saplings growing in particularly shady areas, there is not enough sunlight reaching their leaves to perform adequate photosynthesis. For survival, the sapling relies on nutrients and sugar from older, taller trees sent through the mycorrhizal network. A study on Douglas-fir trees at England’s University of Reading, indicates that trees recognize the root tips of their relatives and favor them when sending carbon and nutrients through the fungal network.
Ecologist Suzanne Simard hypothesizes that the fungus linking the trees is motivated by the need to secure its own source of carbon. The mycorrhizal network plays a distribution role to keep the mycelium-connected trees alive and healthy and the fungi’s supply of carbon consistent. As a sort of payment for their services, the mycorrhizal network retains about 30% of the sugar that the connected trees generate through photosynthesis. The sugar fuels the fungi, which in turn collects phosphorus and other mineral nutrients into the mycelium, which are then transferred to and used by the trees.
Mother Trees
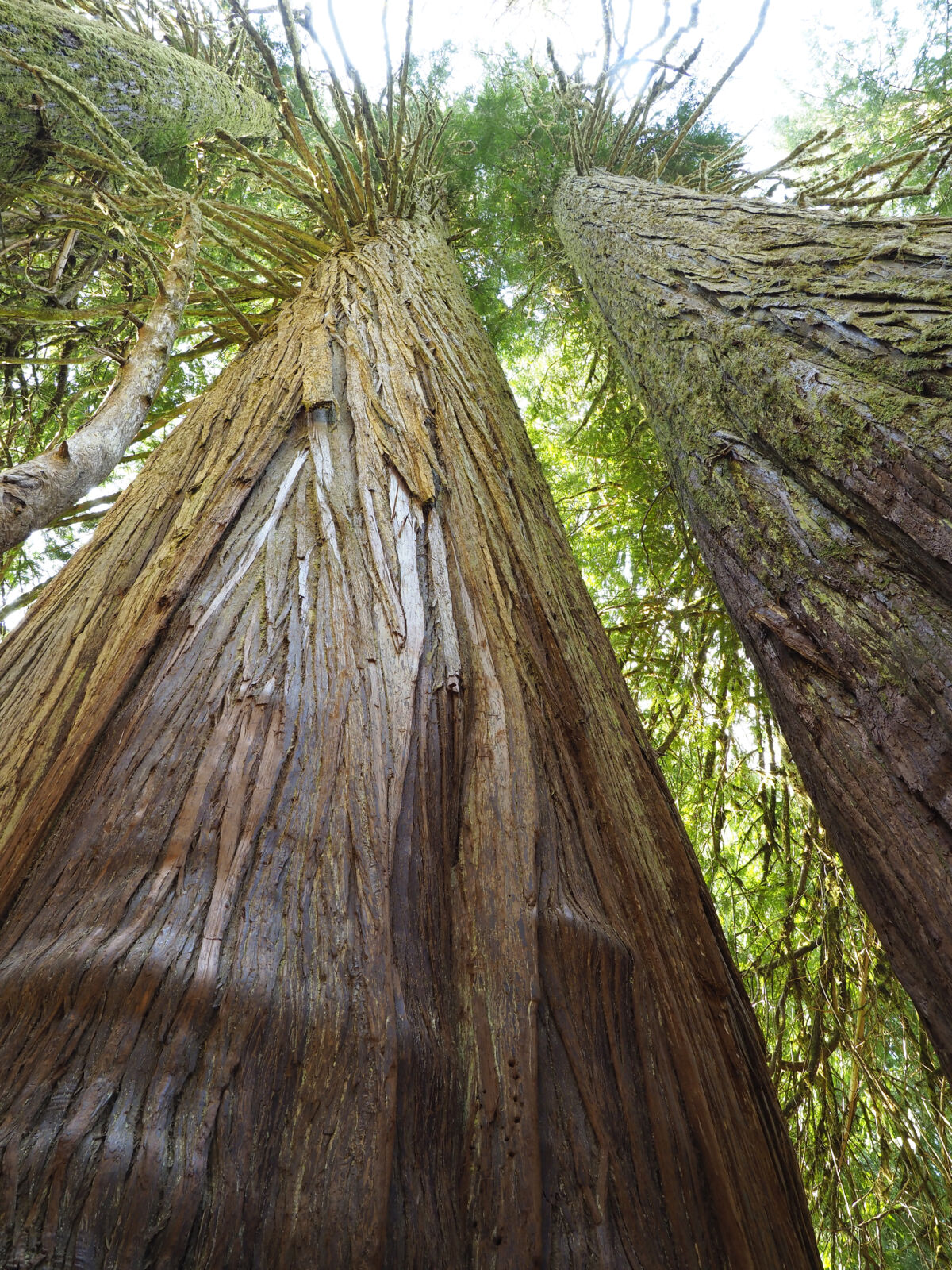

A linchpin in the tree-fungi networks are hub trees. Also referred to as “mother trees,” these are the older, more seasoned trees in a forest. Typically, they have the most fungal connections. Their roots are established in deeper soil, and can reach deeper sources of water to pass on to younger saplings. Through the mycorrhizal network, these hub trees detect the ill health of their neighbors from distress signals, and send them needed nutrients.
These findings suggest trees have developed complex symbiotic relationships for species survival. The mycorrhizal network is an integral part of this connectivity, and while the fungi are often acting in their own best interests, they facilitate health and survival of even the biggest trees.
Next time you’re visiting a forest, as you wander through the trees, take a moment to think about the complex exchanges happening underneath your feet. The mycorrhizal network is critical to supplying the life-giving nutrients that keep our forests healthy.

Next time you’re visiting a forest, as you wander through the trees, take a moment to think about the complex exchanges happening underneath your feet. The mycorrhizal network is critical to supplying the life-giving nutrients that keep our forests healthy.
https://www.nationalforests.org/blog/underground-mycorrhizal-network






